When dealing with respiratory issues or dry air conditions, two devices often come to mind: nebulizers and humidifiers. While both involve moisture and can benefit breathing, they serve distinctly different purposes and operate through different mechanisms.
Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about respiratory health and home comfort.
Download our free guide that has over 100+ of the best tips for healthy lungs.
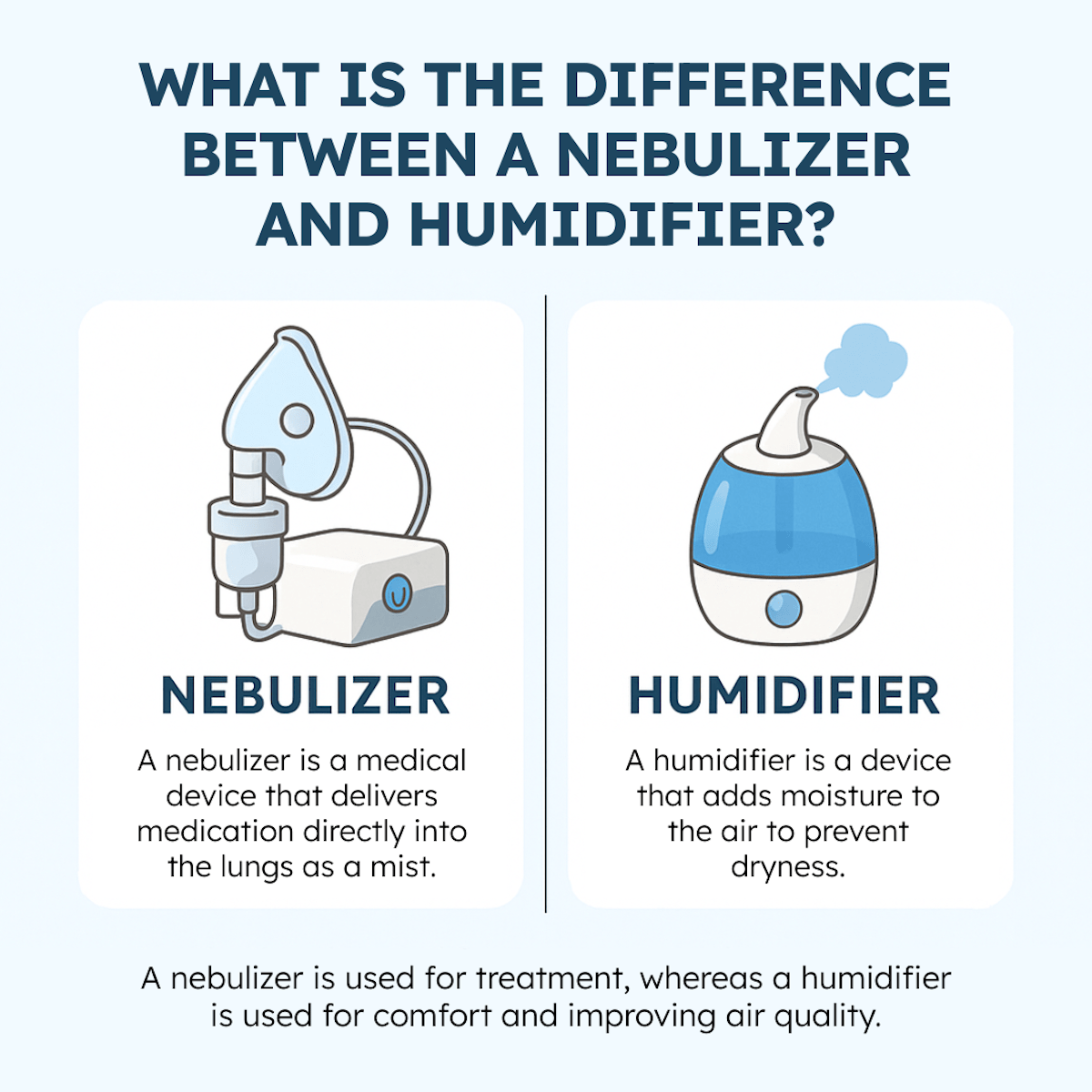
What is the Difference Between a Nebulizer and a Humidifier?
A nebulizer and a humidifier both produce mist but serve different purposes. A nebulizer is a medical device that delivers medication directly into the lungs by converting liquid medicine into a fine mist for inhalation, typically used for conditions such as asthma, COPD, or other respiratory conditions. In contrast, a humidifier adds moisture to the air, preventing dryness that can irritate the skin, throat, and nasal passages, especially in dry environments.
While both can ease breathing, nebulizers are used for treatment, whereas humidifiers are used for comfort and improving air quality. They are not interchangeable and should be used for their intended purposes.
What is a Nebulizer?
A nebulizer is a medical device used to deliver medication directly into the lungs in the form of a mist. It transforms liquid medicine into a fine aerosol, making it easy to inhale through a mouthpiece or face mask.
Nebulizers are commonly prescribed for individuals with respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other lung disorders. This method ensures that the medicine reaches the airways quickly and efficiently, providing fast relief from symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.

How Nebulizers Work
Nebulizers use compressed air, ultrasonic waves, or mesh technology to break down liquid medication into microscopic particles. These particles are small enough (typically 1-5 micrometers) to reach the deepest parts of the lungs, including the alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
There are three main types of nebulizers:
- Jet Nebulizers use compressed air to create a high-velocity gas stream that breaks up the medication. They’re the most common type and are reliable for most medications.
- Ultrasonic Nebulizers use high-frequency sound waves to create vibrations that turn liquid medication into mist. They tend to be quieter but may not be suitable for all types of medications.
- Mesh Nebulizers use a vibrating mesh with thousands of tiny holes to create fine particles. They’re portable, quiet, and efficient, but are typically more expensive.
Medical Uses of Nebulizers
Nebulizers are prescribed for various respiratory conditions, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and other lung diseases. Common medications administered through nebulizers include bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, and mucolytic agents.
Note: The direct delivery method ensures that medication reaches the lungs quickly and effectively, often providing faster relief than oral medications.
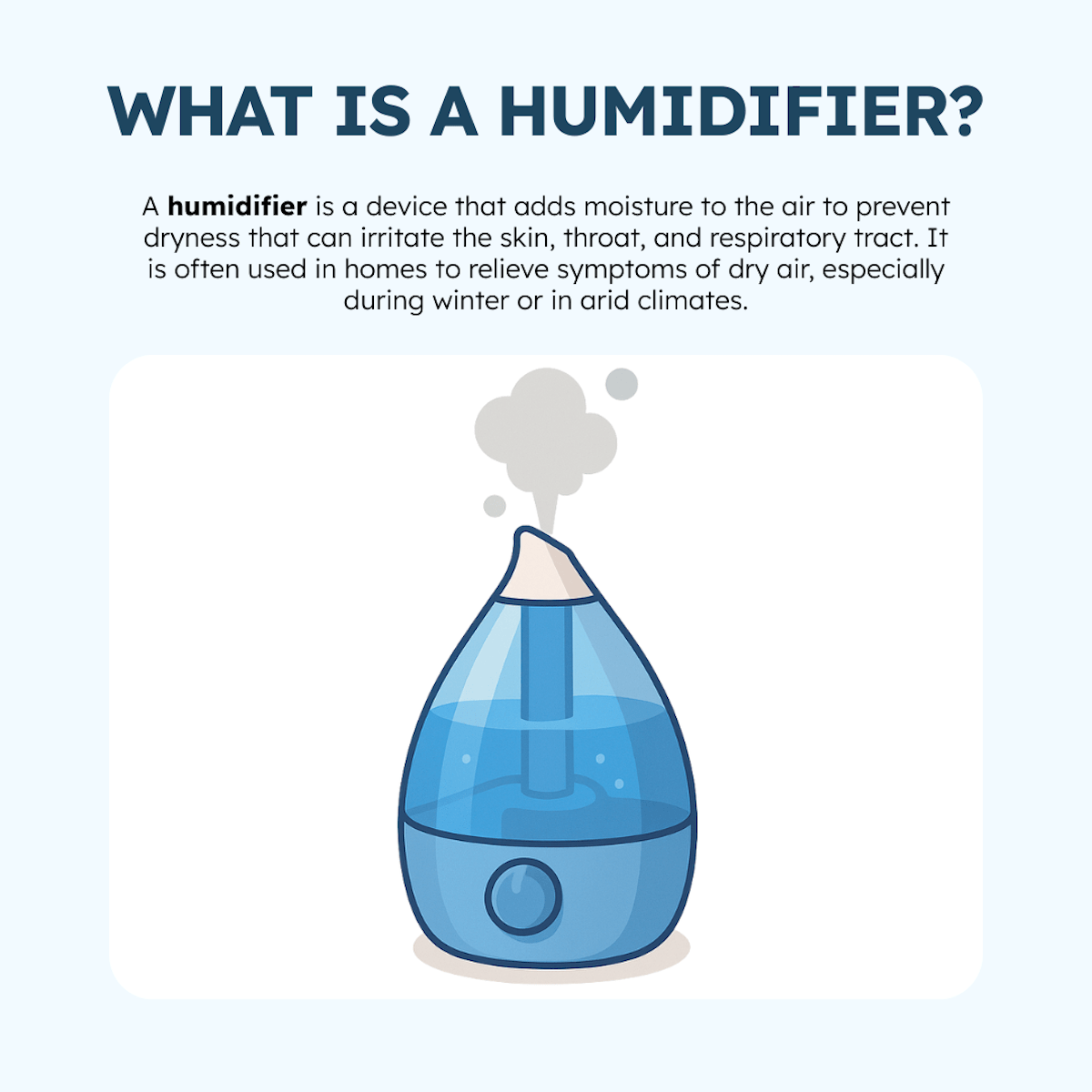
What is a Humidifier?
A humidifier is a device that adds moisture to the air, thereby increasing humidity levels in a room or home. It’s especially useful during dry seasons or in areas with low humidity, where the air can cause dry skin, irritated sinuses, sore throats, or respiratory discomfort.
By releasing a cool or warm mist, a humidifier helps create a more comfortable and breathable environment. It’s not a medical device, but it can support overall wellness by reducing dryness that may aggravate symptoms of allergies, colds, or other conditions.
How Humidifiers Work
Humidifiers add water vapor to the air through various methods, depending on their type:
- Cool mist humidifiers include evaporative and ultrasonic models. Evaporative humidifiers use a fan to blow air through a wet wick or filter, while ultrasonic models use high-frequency vibrations to create a fine water mist.
- Warm mist humidifiers heat water to create steam, which then cools slightly before being released into the air. They can help kill bacteria and mold in the water, but they use more energy.
- Whole-house humidifiers are integrated into HVAC systems to maintain humidity levels throughout an entire home.
Benefits of Proper Humidity
Maintaining indoor humidity between 30% and 50% can provide numerous benefits, including reduced static electricity, preserved wooden furniture and flooring, improved skin and hair health, and potentially reduced transmission of airborne viruses.
Note: Proper humidity can also make breathing more comfortable, especially during winter months when heating systems dry out indoor air.
Key Differences Between Nebulizers and Humidifiers
- Purpose and Function: The fundamental difference lies in their intended use. Nebulizers are medical devices that deliver medication to treat specific respiratory conditions, while humidifiers are comfort devices that improve overall air quality by adding moisture.
- Target Area: Nebulizers deliver medication directly to the respiratory system through inhalation, targeting the lungs specifically. Humidifiers affect the ambient air in a room or building, creating environmental changes that can benefit everyone in the space.
- Liquid Used: Nebulizers require specific medications prescribed by healthcare providers, often including bronchodilators, steroids, or antibiotics. Humidifiers use plain water, though some people add essential oils (though this isn’t recommended for all types).
- Particle Size and Delivery: Nebulizers create extremely fine particles (1-5 micrometers) designed to penetrate deep into lung tissue. Humidifiers produce larger water droplets that increase ambient humidity rather than being designed for inhalation.
- Medical Supervision: The use of a nebulizer requires medical supervision, a proper prescription, and specific instructions from healthcare providers. Humidifiers can be purchased and used without a medical consultation, although proper maintenance is essential for safety.
When to Use Each Device
Nebulizer Usage
Nebulizers should only be used when prescribed by a healthcare provider for specific medical conditions.
They’re typically recommended for patients with asthma who need quick relief, individuals with COPD requiring regular medication delivery, children who have difficulty using inhalers properly, or patients with severe respiratory infections requiring antibiotic treatment.
Humidifier Usage
Humidifiers are beneficial when indoor humidity falls below 30%, during winter months when heating systems dry the air, in arid climates with naturally low humidity, or when experiencing symptoms of dry air, such as dry skin, a scratchy throat, or static electricity.
They can also be helpful for people with certain respiratory conditions, but this should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Safety Considerations
Nebulizer Safety
Proper cleaning and maintenance are crucial to prevent bacterial growth and contamination. Users should follow healthcare provider instructions exactly, never share nebulizers with others, replace parts as recommended, and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or don’t improve.
Humidifier Safety
Regular cleaning prevents the growth of mold and bacteria that could be dispersed into the air. Users should change water daily, clean the device regularly according to the manufacturer’s instructions, use distilled water to prevent mineral buildup, and monitor humidity levels to avoid over-humidification, which can promote mold growth.
Maintenance Requirements
Both devices require regular maintenance for safe and effective operation. Nebulizers need daily cleaning after use, weekly deep cleaning, and periodic replacement of tubing, masks, and medication cups.
Humidifiers require daily water changes, regular cleaning to prevent biofilm formation, and filter replacement when applicable.
Cost Considerations
Nebulizers typically require higher upfront costs and ongoing expenses for medications and replacement parts. Insurance often covers nebulizers and medications when prescribed for medical conditions.
Humidifiers have lower initial costs and minimal ongoing expenses, mainly electricity and occasional filter replacements.
Making the Right Choice
The choice between a nebulizer and a humidifier isn’t typically an either-or decision, as they serve different purposes. Nebulizers are medical necessities for individuals with specific respiratory conditions and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Humidifiers are comfort devices that can benefit general health and comfort, but aren’t substitutes for medical treatment.
If you’re experiencing respiratory symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether medical treatment is necessary. For general comfort and improved air quality, a humidifier can be beneficial, especially in dry climates or during winter months.
FAQs About Nebulizers and Humidifiers
Are Nebulizers the Same as Humidifiers?
No, nebulizers and humidifiers are not the same. Although both release mist into the air, they serve entirely different purposes. A nebulizer is a medical device used to deliver medication directly to the lungs, typically for the management of respiratory conditions such as asthma or COPD.
In contrast, a humidifier is a household appliance that increases moisture in the air to relieve dryness in the skin, throat, and nasal passages. While both may benefit respiratory comfort, only the nebulizer provides targeted treatment.
Which Is Better, a Humidifier or a Nebulizer?
It depends on your needs. A nebulizer is better suited for delivering medication directly to the lungs to treat conditions such as asthma, COPD, or bronchitis. A humidifier, on the other hand, is best suited for adding moisture to dry indoor air, thereby relieving general discomfort, such as dry skin or irritated sinuses.
While both can support respiratory comfort, only nebulizers provide targeted treatment. Consult a healthcare provider to determine which is most appropriate for your situation.
Can I Put My Nebulizer Meds in a Humidifier?
No, you should never put nebulizer medications in a humidifier. Nebulizers are specifically designed to convert liquid medication into a fine mist that can be inhaled directly into the lungs. Humidifiers are not built to handle medications and cannot deliver them effectively or safely.
Doing so could damage the device or pose health risks. Always use medications only as directed and with the proper equipment. If you’re unsure how to use your nebulizer, consult your healthcare provider.
Do Humidifiers Help with Asthma?
Humidifiers can help alleviate dryness in the airways, which may ease discomfort for some individuals with asthma, particularly in dry climates or heated indoor spaces. However, too much humidity can lead to mold, mildew, and dust mites—common asthma triggers.
Therefore, maintaining indoor humidity between 30% and 50% is essential. While a humidifier may offer symptom relief, it’s not a treatment for asthma. It’s best to consult a healthcare provider before using one as part of asthma management.
Which Is Better: Steam Inhalation or Nebulizer?
The choice depends on your condition. Steam inhalation—breathing in warm water vapor—can temporarily relieve nasal and sinus congestion, often helping with cold or flu symptoms. However, it doesn’t deliver medication or penetrate the lower airways effectively.
A nebulizer, on the other hand, delivers medicated mist directly into the lungs and is more suitable for serious respiratory conditions, such as asthma or COPD. If prescribed a nebulizer, always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for proper use.
What Is the Purpose of a Humidifier?
A humidifier adds moisture to indoor air, helping to relieve symptoms caused by dry environments. Common benefits include relief from dry skin, nasal irritation, sore throat, and sinus congestion, especially during winter months when heating systems dry out the air.
Note: While it can contribute to overall comfort, a humidifier does not treat respiratory illnesses and should be used with caution to avoid excessive humidity.
What Is the Purpose of a Nebulizer?
A nebulizer is a medical device designed to deliver aerosolized medication directly into the lungs. It’s primarily used for treating respiratory conditions such as asthma, COPD, bronchitis, or other lung disorders.
By delivering medication directly to the airways, it acts quickly and effectively, making it a preferred method for individuals who have difficulty using inhalers or require rapid symptom relief.
Can Nebulizers and Humidifiers Be Used Together?
Yes, nebulizers and humidifiers can be used together, but with caution. A nebulizer provides medication, while a humidifier improves air moisture levels. When used in combination, they may enhance respiratory comfort, especially in dry environments.
However, over-humidification can lead to the buildup of mold and allergens, which may exacerbate symptoms for individuals with asthma or allergies. Always monitor humidity levels and consult a healthcare provider before using both devices regularly.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between nebulizers and humidifiers is essential for making informed decisions about respiratory health and home comfort.
While both devices involve moisture and can impact breathing, nebulizers are specialized medical devices designed to deliver medication for treating specific conditions, whereas humidifiers are general-purpose devices intended to improve air quality and comfort.
Neither device should be viewed as a cure-all for respiratory problems. Persistent breathing difficulties, coughing, or other respiratory symptoms warrant consultation with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment. When used appropriately and maintained properly, both nebulizers and humidifiers can play vital roles in maintaining respiratory health and promoting comfort.
Written by:
John Landry is a registered respiratory therapist from Memphis, TN, and has a bachelor's degree in kinesiology. He enjoys using evidence-based research to help others breathe easier and live a healthier life.
References
- Fink JB, Stapleton KW. Nebulizers. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2024.
- Byber K, Radtke T, Norbäck D, Hitzke C, Imo D, Schwenkglenks M, Puhan MA, Dressel H, Mutsch M. Humidification of indoor air for preventing or reducing dryness symptoms or upper respiratory infections in educational settings and at the workplace. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021.


